USB RFID reader
DO RFID Reader manufacturer is the largest USB RFID reader manufacturer.
Our USB RFID Reader writers offer consistency in high performance and functionality needed and cheap cost for use in any successful RFID system.
The RFID card Reader is a radio frequency transmitter and receiver which reads and writes information to an RFID tag or RFID card in order to identify, categorize and track assets.
USB RFID Readers are small, lightweight reader that are perfect for desktop applications. USB RFID readers can identify objects quicker, more accurately, at a reduced overall cost, and at various points of the object’s lifecycle.
D.O RFID Reader manufacturer produce almost every USB RFID reader 125khz , 134.2 khz RFID reader usb,usb 13.56 mhz RFID reader writer,HF RFID mifare card reader usb 13.56 mhz 14443a,USB RFID reader writer,usb rfid reader keyboard emulation,NFC RFID reader usb,13.56mhz ,860mhz-960mhz on the market.
All these USB RFID readers support windows systems and no need driver. Our USB RFID scanner is offered in various form factors with many capabilities, such as laser, imager, handheld, fixed, Bluetooth, USB, UHF, HF, iOS/Android Compatible, and more! From warehousing to the office, D.O RFID reader manufacturer supply all RFID reader-writers that can help you deliver accurate and reliable reading for any environment.
USB RFID Readers are ideal for desktop and read/write applications. It is a lower cost RFID reader when compared to RFID handheld reader scanner or fixed readers. All you need is a desktop or PC and we can provide you with the reader and application development tools to get started.
Selection of Long Range RFID Readers
Let's us know if you didn't find out what you need.
USB RFID reader 125Khz
It is high performance 125Khz RFID smart card reader without driver, the read distance up to 80mm,...View Details

125khz RFID reader writer
125khz RFID reader writer able read write 125khz RFID card and tag...View Details

USB 13.56 mhz RFID reader writer
DOR20 is USB 13.56 mhz RFID reader writer device that one type simple, easy to operate, stable, low cost, and high performance...View Details
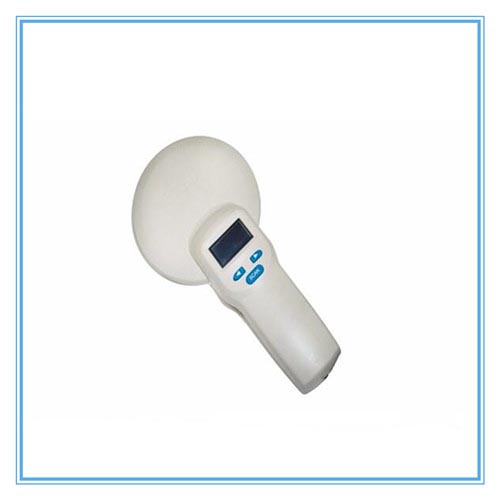
Animal RFID tag reader
Animal RFID Reader works with animal ear tag, glass tag for for animal tracking ....View Details

USB RFID card reader writer
USB RFID card reader-writer can read and write ISO14443A, ISO14443 B, and ISO15693 standard cards, ....View Details

RFID UHF reader writer
Desktop USB RFID UHF reader writer is portable rfid reader writer for program ....View Details
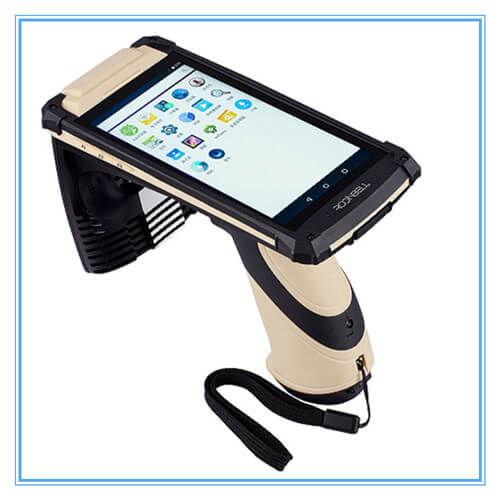

RFID handheld reader
This RFID handheld reader is passive UHF long range data collection terminal ....View Details
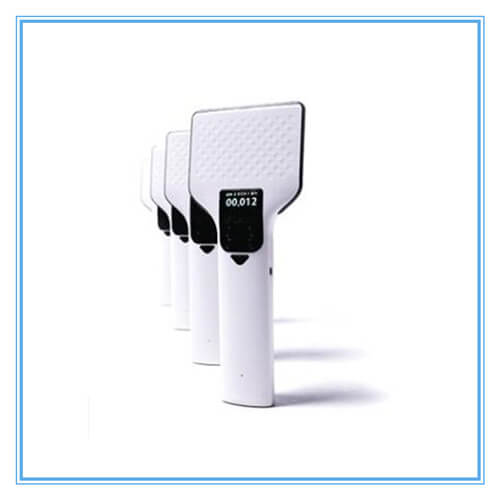

Handheld RFID Reader
The Handheld RFID Reader is UHF RFID Handheld bluetooth reader which is designed with high performance ....View Details

USB HF RFID Reader
RFID reader with USB interface is very cheap for RFID desktop applications. usb hf rfid reader writer with virtual keyboard input....View Details
Request A Quote or Samples

In enterprise environments, RFID systems are rarely built from scratch. They are integrated into existing software platforms, production lines, access control systems, or asset management workflows. In this context, USB RFID readers have become one of the most widely adopted RFID devices, largely because they rely on universal, standardized technologies that minimize integration cost and deployment risk.
For B2B buyers, the value of a USB RFID reader is not just in its ability to read RFID tags. Its real strength lies in the common technologies it adopts—technologies that ensure compatibility, scalability, and long-term usability across different industries and system architectures.
This article explains what a USB RFID reader is, how it works, and—most importantly—which universal technologies it uses and why those technologies matter for professional procurement decisions.
What Is a USB RFID Reader?
A USB RFID reader is an RFID reading device that connects to a host system—such as a PC, industrial computer, POS terminal, or embedded controller—via a Universal Serial Bus (USB) interface. It reads data from RFID tags or cards and transmits that data to the host system for processing.
Unlike standalone or network-based readers, USB RFID readers are typically used in desktop, kiosk, workstation, and industrial terminal environments, where simplicity, stability, and compatibility are priorities.
From a B2B perspective, USB RFID readers are favored because they are:
- Easy to deploy
- OS-agnostic or OS-friendly
- Cost-effective for bulk installation
- Highly compatible with existing systems
Core Universal Technologies Used in USB RFID Readers
1. USB Interface Standard (USB 2.0 / USB HID)
At the foundation of every USB RFID reader is the USB standard itself, one of the most widely adopted communication technologies in the world.
Most USB RFID readers use USB 2.0, which provides sufficient bandwidth, stable power delivery, and universal compatibility across operating systems.
More importantly, many USB RFID readers support USB HID (Human Interface Device) mode.
Why USB HID Matters for B2B Buyers
USB HID allows the RFID reader to behave like a keyboard. When a tag is scanned, the ID is sent to the host system as if it were typed on a keyboard.
This brings several advantages:
- No driver installation required
- Works with Windows, Linux, macOS, and embedded systems
- Compatible with almost any software that accepts keyboard input
- Extremely low IT deployment cost
For enterprises, USB HID is a universal integration shortcut.
2. Standard RFID Frequencies (LF, HF, UHF)
USB RFID readers are built around globally standardized RFID frequency bands. These frequencies are regulated and widely supported, making them safe choices for long-term projects.
Common options include:
- LF (125 kHz / 134.2 kHz)
Used for animal identification, access control, and industrial tagging. - HF (13.56 MHz)
The most common frequency for access cards, NFC, libraries, payment, and identification systems. - UHF (860–960 MHz)
Used for long-range reading in logistics, warehousing, and asset tracking.
By adhering to these international frequency standards, USB RFID readers ensure:
- Legal operation in target markets
- Compatibility with existing RFID tags and cards
- Easier system expansion in the future
3. ISO and Industry RFID Protocol Standards
Another key “universal technology” behind USB RFID readers is compliance with ISO standards.
Depending on frequency, a professional USB RFID reader may support:
- ISO 14443 (HF contactless cards, NFC)
- ISO 15693 (vicinity cards)
- ISO 11784/11785 (animal identification)
- EPC Gen2 / ISO 18000-6C (UHF RFID)
For B2B buyers, ISO compliance reduces vendor lock-in. It allows organizations to source tags, cards, and consumables from multiple suppliers without replacing the reader infrastructure.
4. Keyboard Emulation Technology
Keyboard emulation is one of the most important universal technologies in USB RFID readers.
Instead of requiring a custom SDK or middleware, the reader outputs tag data as plain text input. This allows it to work instantly with:
- ERP systems
- Access control software
- Warehouse management systems
- Web-based platforms
- Custom in-house software
This technology is especially valuable in environments where:
- IT resources are limited
- Software cannot be modified easily
- Fast rollout is required
From a procurement standpoint, keyboard emulation dramatically reduces integration risk.
5. Cross-Platform Operating System Compatibility
USB RFID readers rely on standard USB device classes, which are natively supported by most operating systems.
Typical compatibility includes:
- Windows (all major versions)
- Linux
- macOS
- Android (with OTG support)
- Embedded and industrial OS platforms
This OS-level universality makes USB RFID readers ideal for:
- Multi-site deployments
- International projects
- Mixed hardware environments
6. Standard Power Supply via USB
Another overlooked but critical universal technology is USB power delivery.
USB RFID readers are powered directly through the USB port, eliminating the need for:
- External power adapters
- Additional wiring
- Power certification complexity
This simplifies installation and makes the reader suitable for:
- Desktop environments
- Kiosks
- Industrial terminals
- Portable setups
For large-scale deployments, fewer power components mean lower failure rates and easier maintenance.
7. Modular Firmware Architecture
Professional USB RFID readers use modular firmware designs, allowing support for multiple tag types, protocols, and output formats.
This enables:
- Firmware upgrades without hardware changes
- Custom configuration for different projects
- Long product lifecycle
From a B2B perspective, firmware flexibility protects investment and supports evolving requirements.
Typical B2B Applications of USB RFID Readers
Because of their reliance on universal technologies, USB RFID readers are used across many industries:
- Access control and time attendance
- Asset and inventory management
- Library and document tracking
- Healthcare and laboratory identification
- Manufacturing workstations
- Retail and POS systems
In these scenarios, stability and compatibility matter more than experimental features.
Why Universal Technologies Matter in Bulk Procurement
For B2B buyers, especially those purchasing in volume, technology choices directly affect:
- Deployment speed
- Training cost
- IT support workload
- Long-term maintenance
USB RFID readers built on common, standardized technologies reduce uncertainty. They work predictably, integrate easily, and remain usable even as surrounding systems change.
This is why many system integrators and enterprises prefer USB RFID readers over proprietary or highly customized alternatives.
Customization Without Breaking Compatibility
Although USB RFID readers rely on universal technologies, professional manufacturers can still offer customization, such as:
- Branding and housing design
- Output format configuration
- Firmware feature selection
- Cable and connector options
The key is that customization is done on top of standards, not instead of them
